News
Cardiac pathology refers to diseases that affect the heart and compromise its structure or function. The main cardiac pathologies include heart failure, characterized by the heart's inability to pump blood adequately, leading to symptoms such as shortness of breath and fatigue; arrhythmias, which are changes in the rhythm of the heartbeat; heart valve diseases, which can cause stenosis or valve insufficiency; congenital heart disease, malformations present from birth; and myocarditis, inflammation of the heart muscle generally caused by infections or immune reactions. These conditions can present with a variety of symptoms, including chest pain, palpitations, edema and fatigue, and require specific diagnosis and treatment to avoid serious complications.
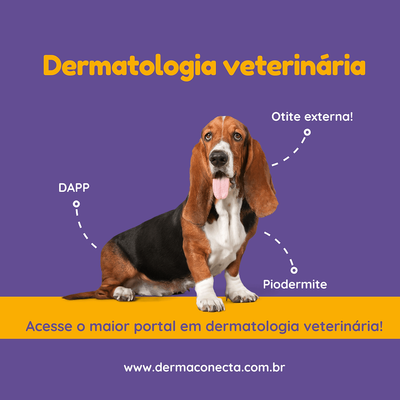
Read MoreVeterinary dermatology is the specialty of veterinary medicine dedicated to the study, diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the skin, hair, nails, ears and their appendages in pets, such as dogs and cats. This area is essential for the health and well-being of pets, as the skin is the largest organ in the body and acts as a protective barrier against external agents. Veterinary dermatologists perform specific tests, such as skin scrapings, cytology, fungal and bacterial cultures, biopsies and allergy tests, to accurately identify the causes of dermatological diseases and apply effective treatments. Veterinary dermatology is one of the fastest-evolving specialties in veterinary medicine, requiring highly trained professionals to deal with the complexity and variety of skin problems in animals.
Read MoreVeterinary renal failure is a serious condition characterized by loss of kidney function, which occurs when approximately 75% of the nephrons responsible for filtering blood stop functioning properly. This disease can be classified into two main types: acute renal failure, which occurs suddenly and can be reversible, and chronic renal failure, which is progressive and irreversible. In animals, especially dogs and cats, renal failure compromises the kidneys' ability to eliminate toxins and maintain fluid and electrolyte balance, leading to symptoms such as loss of appetite, increased thirst and urination, vomiting, weakness and dehydration. Diagnosis is made through laboratory and imaging tests, and treatment aims to control symptoms, slow the progression of the disease and improve the animal's quality of life.
Read MoreEndocrinology is the medical specialty that studies the endocrine glands and the hormones they produce, which are responsible for regulating various functions of the body, such as metabolism, growth, reproduction and mood. Endocrinologists diagnose and treat diseases related to hormonal imbalances, such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, obesity, osteoporosis, among other metabolic and hormonal conditions.
Read MoreVeterinary ophthalmology is the specialty of veterinary medicine dedicated to the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of eye diseases in animals. It covers the care of the eyes of pets such as dogs, cats, birds, rabbits and others, using specific tests to identify conditions such as conjunctivitis, glaucoma, cataracts, corneal ulcers, among others. In addition to clinical treatment, the veterinary ophthalmologist can perform surgical procedures to correct eye problems, ensuring the quality of life and well-being of animals. This area is essential to prevent vision loss and improve the overall health of pets.
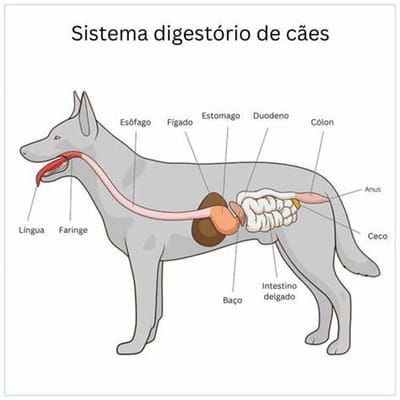
Read MoreVeterinary gastroenterology is the area of veterinary medicine that studies the gastrointestinal tract of animals, including the ingestion, digestion and absorption of food, as well as the functioning of the organs involved, such as the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver and pancreas. It covers the diagnosis and treatment of diseases that affect these organs, which are essential for the nutrition and health of animals. The digestive system varies according to the species, such as in dogs and cats, which have simple stomachs, and in ruminants, such as cattle, which have compartmentalized stomachs for microbial fermentation. The intestinal microbiota is also an important component, influencing the digestive and immunological health of animals.
Read More